An optician’s clinic is a destination for individuals seeking assistance with their vision correction needs. Opticians are specialized professionals who play an integral role in eye care, complementing the work of ophthalmologists and optometrists. They focus on dispensing and fitting prescription eyeglasses, sunglasses, and contact lenses, ensuring that patients receive proper vision aids that match their lifestyle and optical requirements.
At an optician’s clinic, the journey begins with a personal consultation where the optician reviews the patient’s prescription, provided by an optometrist or ophthalmologist. They offer expert advice on the selection of frames and lenses based on factors such as prescription strength, face shape, skin tone, and individual preferences. Moreover, opticians are equipped to perform adjustments and repairs to eyewear, assuring a comfortable and precise fit.
Pre-Examination Procedures
The pre-examination procedures at an optician’s clinic are designed to set the stage for an accurate assessment of a patient’s vision and eye health. They consist of initial administrative tasks, followed by a series of preliminary tests that prepare the patient for their examination.
Patient Reception and Records
Upon arrival, patients are greeted at reception where they provide personal and insurance details. It is crucial to ensure an up-to-date health record, as this can influence eye health. Administrative staff are tasked with verifying patient information and updating medical records, often including:
- Patient Name and Contact Information: Confirmation of correct details.
- Medical History: A review of general health and any medications that might affect vision.
- Previous Eye Health Records: Information about past eye exams, treatments, and prescriptions.
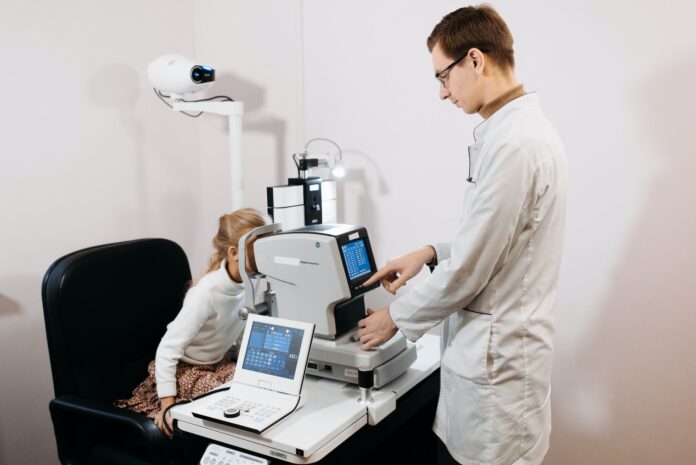
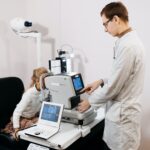
Preliminary Tests
Before the optometrist performs the full eye examination, technicians carry out a series of preliminary tests to determine the baseline of a patient’s eye health.
- Visual Acuity Measurements: To assess the sharpness of vision.
- Autorefraction: A machine estimates the lens prescription needed to correct vision.
- Tonometry: Measurement of intraocular pressure to identify risks of glaucoma, often involving a non-contact “air puff” test.
- Visual Field Testing: To check for any blind spots or peripheral vision issues.
- Pupillary Reactions: Evaluating how pupils respond to light is important for neurological function.
These tests provide a comprehensive overview, enabling the optometrist to conduct a more focused eye exam based on the patient’s unique visual requirements.
Read also: https://www.resolveuganda.org/how-to-find-a-good-optician-essential-tips-for-perfect-vision-care/
Comprehensive Eye Examination
A comprehensive eye examination at an optician’s clinic entails several tests to assess vision clarity and eye health. Patients undergo a series of evaluations to detect any vision corrections needed and potential eye conditions.
Visual Acuity Assessment
The Visual Acuity Assessment is the initial test to measure the sharpness of the patient’s vision. Typically involving a Snellen chart, this test requires patients to read letters from a distance to determine how well they can see at various lengths.
Refraction Test
In the Refraction Test, the optician determines the patient’s prescription for eyeglasses or contact lenses. Using a phoropter, the optician presents a series of lens choices to identify which corrective lenses yield the clearest vision.
Health Evaluation
The Health Evaluation includes several exams to inspect the health of the eyes. Tools like ophthalmoscopes and slit lamps facilitate a detailed examination of the eye’s internal and external structures, checking for signs of conditions such as glaucoma, cataracts, or retinal abnormalities.
The article was written in cooperation with the experts of Glasson – Optician & Optometry Management Software